In some cases, in order to avoid possible singularities,
values ![]() are skipped. Then if
are skipped. Then if
![]() is the number of non-zero data points,
we can evaluate the 'zero-skipping' average as
is the number of non-zero data points,
we can evaluate the 'zero-skipping' average as
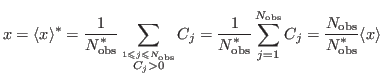
The standard deviation is then
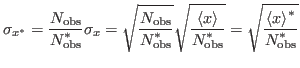
Note that the s.d. is evaluated exactly as if the non-zero