


Next: In what consists the
Up: What happens when I
Previous: What happens when I
Contents
Trimming with noise
The first step in the trimming procedure is to trim with noise (this is often sufficient). This has to be done for all the settings which are foreseen to be used (highgain, standard and fast).
The procedure for the noise trimming is as follows:
- In the Initialization tab click on the settings for which you want to trim (e.g. standard)
- In the Initialization tab click on the advanced radio button to make the trimming accessible.
- In the Acquisition tab set the acquisition time to 100 ms, the repetion to 1 and the delay between frames to 0.
- For noise trimming usually the default parameters
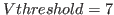 ,
,
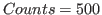 ,
,
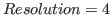 work.
work.
However, to verify the threshold setting it is best to make a threshold scan. To do this go to the Data tab, in the Data display section select the 2D color and type advanced option. In the Acquisition tab select your data directory. Set the number of positions to 0. Select Scan, Type threshold. Typical values for the range are 500 to 900 with a step size of 10. Then click on the start button to perform the threshold scan. After the threhold scan has finished an image similar to the one in 3.7 should be shown. Depending on the system the number of modules may vary. If the plot is similar to the one in 3.10 the noise trim files did already exist and have been loaded when selecting the settings. In this case you don't need to trim with noise again.
Set the parameter Vthreshold in the Trimming box (Initialization tab) 10-30 DAC units below the onset of the noise for the module with the lowest threshold offset. Since the modules have differences in the offset and gain the onset of the noise varies.
You can usually leave the remaining parameters unchanged (Counts/pixel=500; Resolution=4).
- Select the directory where the noise trim files should be written and the filename, to wich will be attached the extension given by the module serial number (.snxxx). If you want the trimfiles to be loaded authomatically when the global settings are selected, select the default directory specified in the config file (or in the ``trimbits/beamline'' directory for the older software versions).
Click on Trim to start the noise trimming process. After the trimming has finished look at the plot and the distribution of the trim bits. The distribution should be around 32
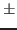 5 and should look gaussian. An example distribution is shown in figure 3.8 and an example plot in 3.9. If the distribution is too much off center change the counts/pixel, if it is too narrow reduce the resolution (set it to 3), if it is too wide increase it (set it to 5). Make sure not too many channels have a trim value of 0 or 63.
5 and should look gaussian. An example distribution is shown in figure 3.8 and an example plot in 3.9. If the distribution is too much off center change the counts/pixel, if it is too narrow reduce the resolution (set it to 3), if it is too wide increase it (set it to 5). Make sure not too many channels have a trim value of 0 or 63.
- Execute the treshold scan again to verify the trimming was done properly. A plot similar tho the one in figure 3.10 should appear.
Figure 3.7:
The untrimmed threshold scan.
|
|
Figure 3.8:
The distribution of the trimbits.
|
|
Figure 3.9:
The trimbits for all the channels.
|
|
Figure 3.10:
The trimmed threshold scan.
|
|
Improve the trimming using X-rays
The improvement of the trimming acquired with noise is not essential: at 12 keV an untrimmed module has a threshold dispersion which is about 1.4 keV and is already reduced to 200 eV at 12 keV by the noise trimming. At lower energies the noise trimming will be more effective, while the threshold dispesion will be still larger at higher energies. The trimming improvement reduces the threshold dispersion to 140 eV at 12 keV and is expected to be almost constant at all energies. For this reason it is suggested to perform the trimming improvement only when a small threshold dispersion is really important (e.g. to avoid flat field corrections or in presence of fluorescent lines close to the threshold value) and it will probably be not worthy at lower energies (i.e. threshold lower than 6 keV and X-ray energy lower than 12 keV).
The procedure for the trimming improvement is as follows:
- Select the settings of the detector and load the noise trimming file
- Set the threshold at half of the X-ray energy (better if the detector has already been calibrated in energy like explained in 3.5)
- Illuminate the detector with a flat field. This is very important to obtain a good trimming.
- Select the acquisition time in the acquisition tab so that there are at least 1000 counts/strip per frame (the more counts, the better trimming). Set the repetions to 1 and the delay between frames to 0.
- Go to expert mode by clicking on advanced in the initialization tab, settings box
- In the trimming box select the directory where the noise trim files should be written and the filename, to wich will be attached the extension given by the module serial number (.snxxx).
- Select the improve method
Start the trimming
If the trimming is correctly performed and the illumination is flat enough, the same trimming can be used every time you will measure at this same energy.
The authomatic loading of energy-specific trim files is not yet implemented.



Next: In what consists the
Up: What happens when I
Previous: What happens when I
Contents
Thattil Dhanya
2019-04-08
![\includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{images/noise_thresholdscanuntrimmed}](img36.png)
![\includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{images/trimbitdistribution}](img37.png)
![\includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{images/trimbitplot}](img38.png)
![\includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{images/noise_thresholdscantrimmed}](img39.png)